The term artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer merely a catchphrase; it is now an integral component of many industries and aspects of our daily lives. AI is expanding beyond automation into the domain of creativity and decision-making, from chatbots that manage customer support to creative tools that produce images, music, or even code. Generative AI and AI agents are two of the most fascinating innovations propelling this change.
However, what are they, how do they function, and what part will they play in technology going forward? Let's take a closer look.

Generative AI: What is it?
Artificial intelligence systems that can produce original content instead of merely analyzing preexisting data are referred to as generative AI. A generative AI model can produce a completely new image of a cat that has never been seen before, as opposed to just identifying a cat in a picture.
Here are some instances of generative AI in action:
- ChatGPT (for text generation that is human-like)
- DALL·E, Stable Diffusion, Mid-Journey (for image generation)
- AlphaCode from DeepMind (for code generation)
- Jukebox (for making music)
Transformers are a type of deep learning that forms the foundation of the majority of contemporary generative AI models. These models can "imagine" or produce new outputs because they are trained on large datasets and acquire patterns, grammar, and context.

AI Agents: What Are They?
AI agents are intelligent systems that can act, make decisions, and interact with their surroundings to accomplish objectives, whereas generative AI produces content.
Consider them as digital workers who think, plan, and act in addition to obeying orders.
Typical components of an AI agent include:
- The capacity to comprehend inputs (text, voice, sensors, etc.) is known as perception.
- Reasoning: Making decisions.
- Action: Performing a task, such as sending an email, getting data, or operating a robot.
- Learning: Using experience to improve performance.
Examples of AI agents in the real world:
- virtual assistants such as Google Assistant, Alexa, and Siri.
- Bots for customer service that can handle problems without the need for human intervention.
- autonomous cars that can navigate and make decisions on their own.
- AI-powered financial trading bots.

AI Agents vs. Generative AI
Despite their overlap, there are some significant distinctions:
| Feature | Generative AI | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Main Role | Creating new content (text, images) | Taking actions to achieve goals |
| Output | Text, code, images, audio | Tasks, decisions, problem-solving |
| Intelligence Type | Creative pattern generation | Goal-driven reasoning & decision-making |
| Examples | ChatGPT, MidJourney | Siri, Tesla Autopilot, Customer bots |
They are even more potent when combined. An AI agent that employs generative AI, for example, could create customized emails, reports, or designs as it carried out tasks in addition to planning them.
The Operation of Generative AI
Typically, generative AI models are constructed using methods like:
- Algorithm layers that imitate the structure of the human brain are called neural networks.
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) systems, which manage long-range linguistic context, are based on transformer models.
- Diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion, are used in image generation to produce realistic images by gradually eliminating noise.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These AI systems, a discriminator and a generator, compete to produce incredibly lifelike results.

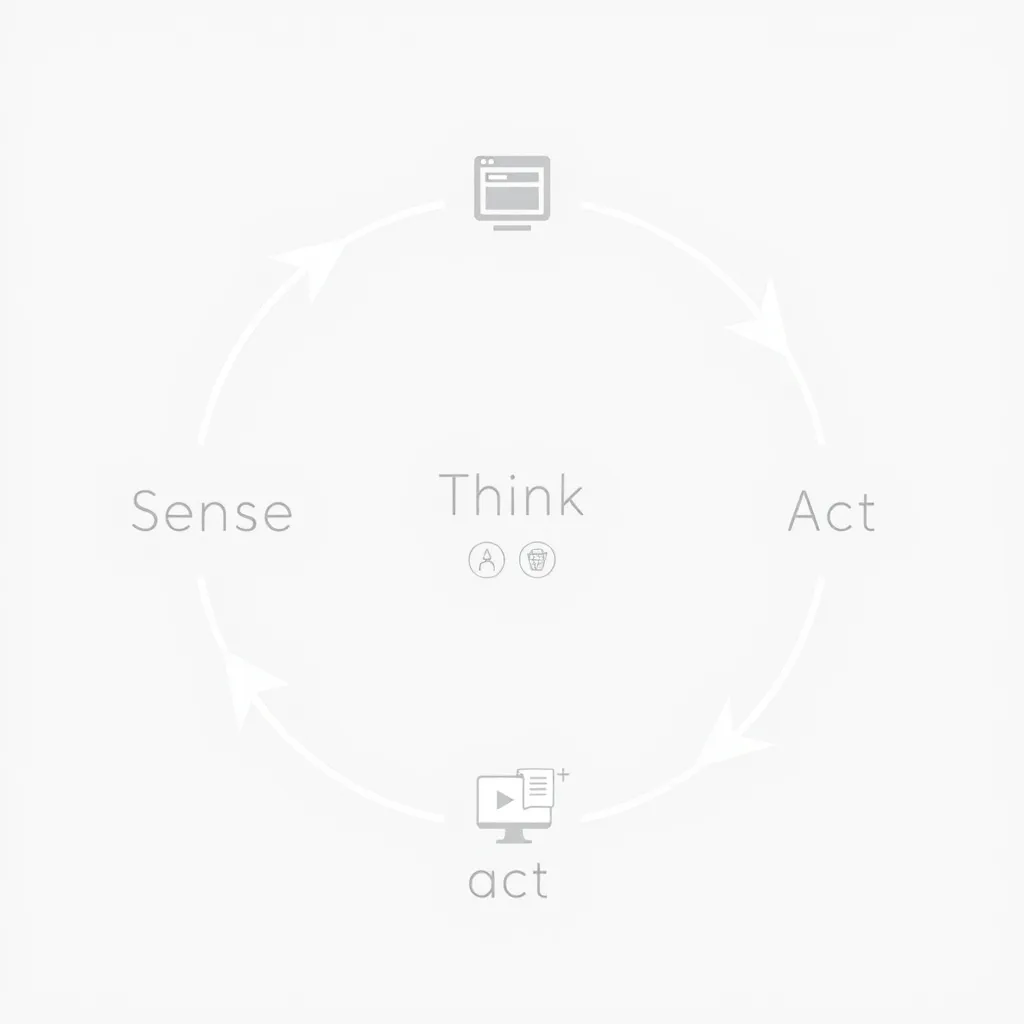
The Operation of AI Agents
AI systems work in a loop:
- Sense: Compile information from the surroundings.
- Think: Make decisions using algorithms (such as reinforcement learning and planning).
- Act: Complete assignments or reply to users.
- Learn: Get better with fresh information or criticism.
An autonomous delivery robot, for instance, can sense the road, plan its path, steer clear of obstructions, and gradually pick up shortcuts.
Applications of Generative AI
All industries are changing as a result of generative AI:
- Content creation includes writing novels, blogs, news summaries, and advertising copy.
- Design: 3D models, product prototypes, and logo development.
- Healthcare: Finding new drugs and creating novel compounds.
- Education: Tutoring and customized learning materials.
- Entertainment: video game worlds, music, and films produced by AI.
- Programming: bug fixes and AI-generated code.

AI Agent Use Cases
AI agents excel at decision-making and automation:
- Customer service: Resolving issues without the need for human assistance.
- Smart Homes: Adapting appliances, lighting, and temperature to user preferences.
- Finance: Risk analysis, automated trading, and fraud detection.
- Healthcare: Helping physicians with patient monitoring, scheduling, and diagnosis.
- Logistics: Supply chain management and self-sufficient delivery.

The Potential of Blending AI Agents with Generative AI
When generative AI and AI agents collaborate, the real magic happens.
Consider the following situation:
"Plan a marketing campaign for my new product," you instruct your AI assistant.
- Researching the audience, creating draft content, and scheduling posts are the steps that the AI agent breaks down the task into.
- The generative AI makes ads, takes pictures, and writes blog entries.
- After that, the AI agent shares the content on various platforms, monitors interaction, and provides findings.
This is creative end-to-end automation.

Advantages of AI Agents and Generative AI
- Efficiency: Human-hour-long tasks can be completed in a matter of seconds.
- Cost Savings: Labor expenses are reduced for businesses.
- Personalization: AI has the ability to customize services or content for specific users.
- Scalability: The ability to manage thousands of tasks at once.
- Innovation: AI comes up with fresh concepts that people might not consider.

Risks and Difficulties
These tools have drawbacks like any other potent technology:
- Bias: Biases in training data may be reflected by generative AI.
- Misinformation includes deceptive content, deepfakes, and phony photos.
- Employment Displacement: Automation may replace some jobs.
- Ethics: Who is the owner of content produced by AI?
- Security Risks: AI systems may be abused or compromised.

AI Agents and Generative AI's Future
In the future, we can anticipate:
- More Autonomous Agents: Without human oversight, AI agents will manage intricate multi-step tasks.
- Improved Human-AI Cooperation: AI will augment human capabilities rather than replace them.
- Hyper-Personalization: Individuals will receive customized goods, services, and instruction.
- Industry Transformation: AI is being used by hospitals to help with surgeries and by law firms to draft contracts.
- Ethics and Regulation: To stop abuse, governments will establish rules.

In conclusion
Two facets of the AI revolution are represented by generative AI and AI agents:
- With the ability to create text, images, music, and more, generative AI fosters creativity.
- AI agents offer autonomy by managing execution and decision-making.
Together, they have the potential to completely transform industries, boost output, and open up new avenues for creativity.
However, this power also carries responsibility: to use these tools responsibly, to avoid prejudices, and to make sure they enhance rather than diminish human potential.
One thing is certain as we approach the dawn of this new era: artificial intelligence will change how we work, live, and envision what is possible by enabling machines that not only think but also create and act.


