Imagine a factory from fifty years ago. Supervisors walk the floor with clipboards to monitor progress, workers assemble products by hand, and machines make loud noises. Imagine a modern factory, where sensors monitor machine performance in real time, robots precisely assemble cars, and supervisors monitor everything from a tablet's digital dashboard. This is the shift from conventional manufacturing to Industry 4.0, which is the era of intelligent manufacturing.
However, what is the true meaning of Industry 4.0? And what impact will it have on future factories? Let's get started.

The Four Revolutions in Industry
We must examine the history of manufacturing in order to comprehend Industry 4.0:
-
The late 1700s and early 1800s saw the first industrial revolution. Factories were powered by steam engines. Manual labor was replaced by mechanization.

-
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the Second Industrial Revolution: Mass production was enhanced by assembly lines and electricity. The model was Henry Ford's automobile assembly line.

-
From the 1970s to the 2000s, the Third Industrial Revolution: Automation and computers made their way into factories. Machines started operating with little assistance from humans.

-
Industry 4.0, or the fourth industrial revolution, began in the 2010s and is still going strong today. AI, IoT, robotics, big data, and cloud computing are examples of smart technologies that turn factories into intelligent, networked systems.

Industry 4.0 is a total rethink of how we design, manufacture, and deliver goods—it's not just an improvement.
Smart Manufacturing: What Is It?
The use of cutting-edge digital technologies to increase factory productivity, adaptability, and decision-making is known as "smart manufacturing."
Consider it this way: In traditional factories, machines operate on their own. Smart factories are made up of people, machines, and sensors that are all connected and exchange data instantly. A well-coordinated orchestra, where each instrument (machine) is aware of the actions of the others, is analogous to a group of individuals.

Industry 4.0's Core Technologies
A few essential technologies form the foundation of the factories of the future:
1. The Internet of Things (IoT)
Machine sensors gather information about vibration, temperature, and speed. This aids in anticipating issues before they result in malfunctions.
Example: To avoid downtime, a conveyor belt sensor alerts engineers if it is overheating.

2. Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI)
AI evaluates machine data to increase productivity, find flaws, and even forecast consumer demand. For instance, AI is able to identify minute flaws in a product that people might overlook.

3. Automation and Robotics
Although they are not new in factories, robots are more intelligent in Industry 4.0. Cobots, or collaborative robots, assist humans in performing hazardous or repetitive tasks. For instance, a cobot lowers the risk of injury by assisting a worker in lifting heavy components.

4. Analytics & Big Data
Large volumes of data are produced by smart factories. Managers can make better decisions more quickly by analyzing this. For instance, data analysis may show that operating machines at a slightly slower speed conserves energy without lowering output.

5. The use of cloud computing
All factory data is uploaded to the cloud and made available from anywhere, rather than being kept on local servers. For instance, a factory manager can use a laptop at home to keep an eye on production in real time.

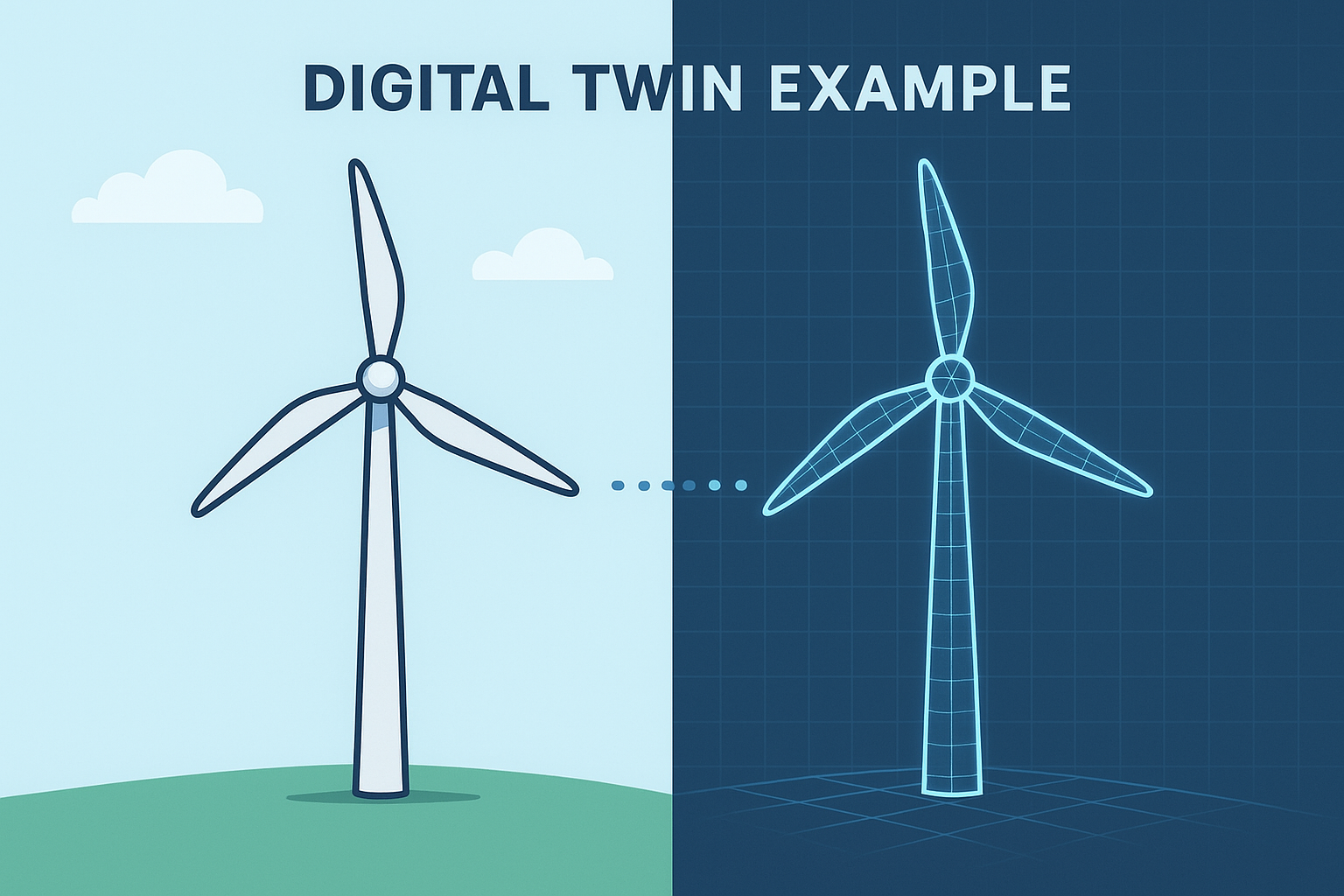
6. Digital Twins
A virtual model of a factory, machine, or product is called a digital twin. Before implementing changes in the real world, engineers can test them on the digital twin.
Example: Before reprogramming a robot, the digital twin is used to check if the change improves efficiency.
7. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)
While VR can train employees in a simulated environment, AR glasses can provide workers with step-by-step instructions.
Example: Instead of reading a manual, a worker wearing AR glasses sees exactly which part to replace in a machine.
Advantages of Intelligent Production
Why should businesses make investments in Industry 4.0? The following are the main advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: By identifying and resolving issues more quickly, machines minimize downtime.
- Improved Quality: AI inspection lowers human error.
- Cost Savings: Energy conservation and breakdown prevention reduce expenses.
- Flexibility: Manufacturers are able to swiftly adjust to shifting consumer needs.
- Safety: By performing risky jobs, robots protect people.
- Sustainability: By optimizing energy use, smart systems lower carbon emissions and waste.
What Will Future Factories Look Like?
Let's fast-forward to 2035. This is how a factory might appear in the future:
- Fully Automated Production: Humans supervise and make creative decisions while robots and machines do the majority of the assembly.
- Zero Downtime: Predictive maintenance makes sure that equipment malfunctions infrequently.
- Self-Optimizing Systems: AI constantly modifies processes to achieve optimal effectiveness.
- Customized Products: Intelligent factories are able to produce customized goods at the same rate as mass production. Consider placing an order for personalized shoes and having them produced in a matter of hours.
- Green manufacturing includes zero waste, recycling, and solar-powered factories.
Industry 4.0's challenges
Even though the future seems exciting, there are obstacles to overcome:
- High Costs: Installing sensors and upgrading machinery can be costly.
- Skills Gap: To operate sophisticated systems, employees require training.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Hackers can target connected factories.
- Job Fears: Some people fear that automation will supplant human labor.
- Data Overload: It's difficult to manage vast volumes of data.
History demonstrates that, despite the loss of previous jobs and opportunities, every industrial revolution generates new ones.

Instances of Intelligent Manufacturing in Operation
- Tesla's Gigafactories: Produce electric vehicles effectively by utilizing robotics, artificial intelligence, and real-time monitoring.
- Siemens: For testing and optimization, the company builds digital twins of whole factories.
- GE Aviation: Creates intricate, lightweight engine parts using 3D printing.
These instances demonstrate that smart manufacturing is both present and expanding.
What Workers Can Expect from Industry 4.0
Will robots replace us in our jobs? This is a major question. In actuality, humans will still be required for the following tasks even though robots will replace repetitive and hazardous jobs:
- Originality
- Solving problems
- Controlling and configuring machinery
- Making decisions
Industry 4.0 might move workers into higher-skilled positions rather than displacing them.
Industry 5.0: The Way Ahead?
Industry 5.0, which is already being discussed, will focus on human-machine collaboration, whereas Industry 4.0 is about smart factories. It emphasizes:
- Customization of goods
- AI combined with human creativity
- Social responsibility and sustainability
Therefore, robots collaborating with humans rather than replacing them is the way of the future for factories.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the future is intelligent. Factories are becoming intelligent ecosystems where data, people, and machines collaborate thanks to Industry 4.0. Future factories will not only produce more quickly and cheaply, but also more intelligently, safely, and environmentally.
Adopting smart manufacturing is essential for businesses to survive, not an option. For employees, it's an opportunity to advance technologically and pick up new skills. Additionally, it's the next step for society toward a future in which sustainability, efficiency, and innovation coexist.
One thing is certain as we move forward into the future: factories of the future are already being constructed today.

